Isostatic and Eustatic Movement
| isostactic_eustatic_sample.docx | |
| File Size: | 15 kb |
| File Type: | docx |
Isostatic and Eustatic Processes
Describe and explain, using an example which you have studied, how rivers adjust to a change in base level. [30]
1
Isostatic uplift is the process by which land rises out of the sea due to tectonic activity. It occurs when a great weight is removed from the land, e.g., the melting of an ice cap.
Eustatic changes are the dropping of sea levels when eater is locked away as ice, and its rising as it melts.
An example of a river I have studied which has experienced and adjusted to a change in base level is the River Nore Co. Kilkenny
There is evidence that the River Nore has experienced a change in base level as there are knickpoints to be found 150 – 200m above sea level.
A knickpoint occurs when there is a drop in sea level, a river is rejuvenated and vertical erosion begins again.
It is the point at which the newly eroded profile meets the old profile and is marked by waterfalls
One may also find several river terraces on the River Nore. With rejuvenation, a river develops a new flood plain at a lower level within the old flood plain. The remnants of the former flood plain are left as steps (terraces). These are called paired river terraces, and if rejuvenation occurs again it can give the river a stepped appearance.
One may also find a clear example of incised meanders at St. Mullins, Co. Kilkenny on the River Nore, these are deep meanders with steep and narrow sides.
2:
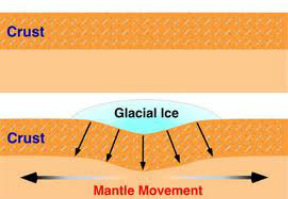
Definition: Isotasy is the vertical movements of the earths crust. (Think of it as the opposite to plate techtonics which is horizontal movements of plates). When weight is put on the crust it falls (Isostatic fall). When weight is taken from the crust it rises (Isostatic Rise)
The last time there was isostatic movements was at the last ice age. Vast amounts of ice were stored on land. This caused:
1. Sea levels to fall (Water was stored on land)
2. Crust levels to fall (The weight of the ice pushed it down)
When the ice age finished the glaciers melted and massive volumes of water flowed into the sea.
This caused:
1. Sea Levels to Rise (Water flowed into sea)
2. Land levels to Rise (Weight was released)
There is much evidence to prove isostatic movements
affected Ireland in the past.
Explain two of the following preferably with diagrams:
1. Knickpoint
2. Raised Terraces
3. Incised Meanders
4. Raised Beaches/Caves
Isostatic uplift is the process by which land rises out of the sea due to tectonic activity. It occurs when a great weight is removed from the land, e.g., the melting of an ice cap.
Eustatic changes are the dropping of sea levels when eater is locked away as ice, and its rising as it melts.
An example of a river I have studied which has experienced and adjusted to a change in base level is the River Nore Co. Kilkenny
There is evidence that the River Nore has experienced a change in base level as there are knickpoints to be found 150 – 200m above sea level.
A knickpoint occurs when there is a drop in sea level, a river is rejuvenated and vertical erosion begins again.
It is the point at which the newly eroded profile meets the old profile and is marked by waterfalls
One may also find several river terraces on the River Nore. With rejuvenation, a river develops a new flood plain at a lower level within the old flood plain. The remnants of the former flood plain are left as steps (terraces). These are called paired river terraces, and if rejuvenation occurs again it can give the river a stepped appearance.
One may also find a clear example of incised meanders at St. Mullins, Co. Kilkenny on the River Nore, these are deep meanders with steep and narrow sides.
2:
Definition: Isotasy is the vertical movements of the earths crust. (Think of it as the opposite to plate techtonics which is horizontal movements of plates). When weight is put on the crust it falls (Isostatic fall). When weight is taken from the crust it rises (Isostatic Rise)
The last time there was isostatic movements was at the last ice age. Vast amounts of ice were stored on land. This caused:
1. Sea levels to fall (Water was stored on land)
2. Crust levels to fall (The weight of the ice pushed it down)
When the ice age finished the glaciers melted and massive volumes of water flowed into the sea.
This caused:
1. Sea Levels to Rise (Water flowed into sea)
2. Land levels to Rise (Weight was released)
There is much evidence to prove isostatic movements
affected Ireland in the past.
Explain two of the following preferably with diagrams:
1. Knickpoint
2. Raised Terraces
3. Incised Meanders
4. Raised Beaches/Caves
